⭐文章目录⭐
👇
Binomial Tree
Here is an example of a binomial tree:
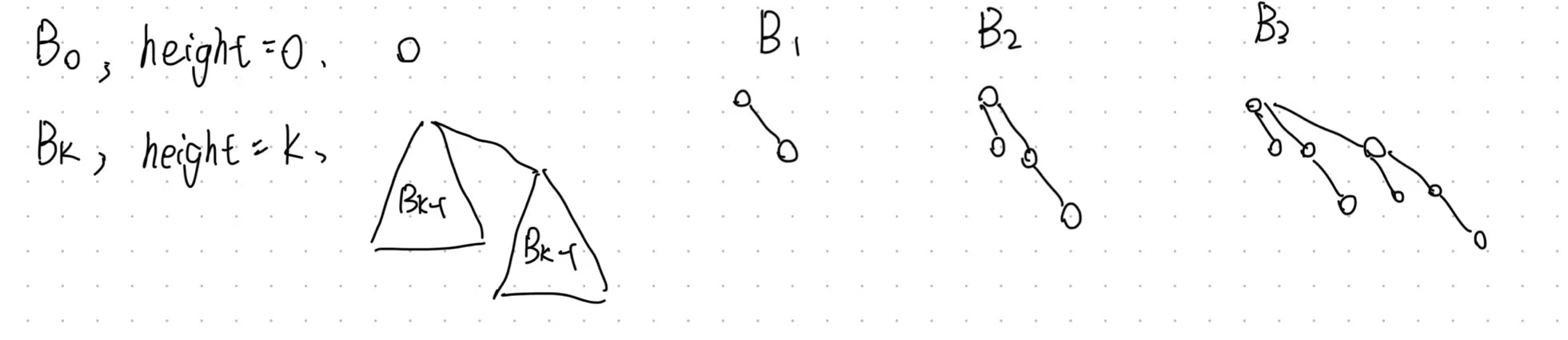
Definition
- A binomial tree $B_k$ is a tree with a height of k,which is generated by attaching $B_{k-1}$ to another $B_{k-1}$.
Theorem
- The number of children of the root of $B_k$ is $k$.
- The number of nodes in $B_k$ is $2^k$.
- The number of nodes at depth d at $B_k$ is $C_k^d$.
Binomial Queue(Heap)
Definition
- A binomial heap is a collection of binomial trees.
- Binomial trees in a binomial heap have different heights.
- Each of Binomial Trees satisfies the heap property.
Here is an example of a binomial heap:
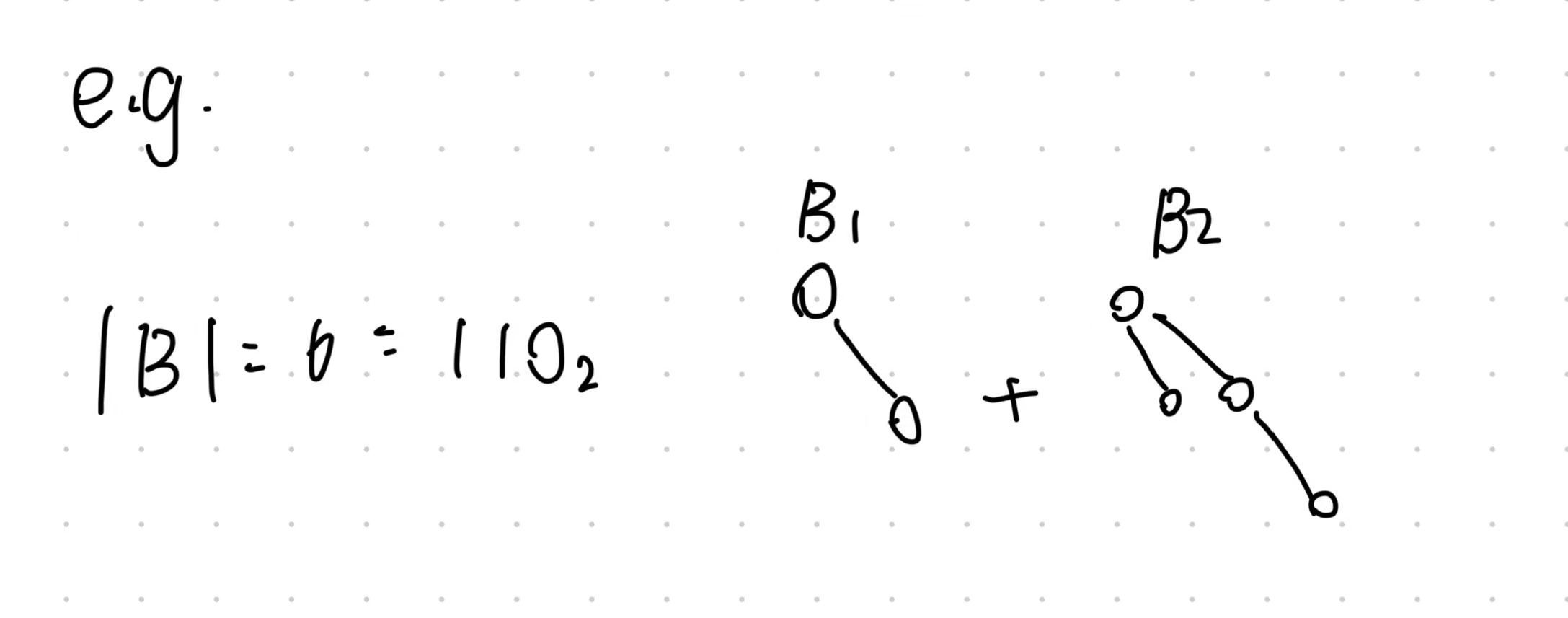
Lemma
- Number of Trees in a n-nodes binomial heap is under $log_2(n)$.
- $N$ insertions into an empty binomial heap takes $O(n)$ time.
- findmin(): $O(logn)$($O(1)$ with a pointer to the min root)
- 1.1.find the $B_k$ with minimum root key.
- 2.Return the minimum key.
- insert(): $O(logn)$
- merge($H_1, H_2$): $O(logn)$
- 1.Let $k_1$ and $k_2$ be the max height of $H_1$ and $H_2$ respectively.
- 2.For i in range(max($k_1, k_2$)):
- 3.IF $B_i$ has two trees,combine them into one tree.
- deletemin(): $O(logn)$
- 1.find the $B_k$ with minimum root key.
- 2.H = H - $B_k$
- 3.H’ = $B_K$ - root
- 4.merge(H, H’)
- decreasekey($x, k$): $O(logn)$
- Do as normal heap does.
- delete($x$): $O(logn)$
- 1.decreasekey($x, \infty$)
- 2.deletemin()
BinQueue Merge( BinQueue H1, BinQueue H2 )
{ BinTree T1, T2, Carry = NULL;
int i, j;
if ( H1->CurrentSize + H2-> CurrentSize > Capacity ) ErrorMessage();
H1->CurrentSize += H2-> CurrentSize;
for ( i=0, j=1; j<= H1->CurrentSize; i++, j*=2 ) {
T1 = H1->TheTrees[i]; T2 = H2->TheTrees[i]; /*current trees */
switch( 4*!!Carry + 2*!!T2 + !!T1 ) {
case 0: /* 000 */
case 1: /* 001 */ break;
case 2: /* 010 */ H1->TheTrees[i] = T2; H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL; break;
case 4: /* 100 */ H1->TheTrees[i] = Carry; Carry = NULL; break;
case 3: /* 011 */ Carry = CombineTrees( T1, T2 );
H1->TheTrees[i] = H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL; break;
case 5: /* 101 */ Carry = CombineTrees( T1, Carry );
H1->TheTrees[i] = NULL; break;
case 6: /* 110 */ Carry = CombineTrees( T2, Carry );
H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL; break;
case 7: /* 111 */ H1->TheTrees[i] = Carry;
Carry = CombineTrees( T1, T2 );
H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL; break;
} /* end switch */
} /* end for-loop */
return H1;
}
ElementType DeleteMin( BinQueue H )
{ BinQueue DeletedQueue;
Position DeletedTree, OldRoot;
ElementType MinItem = Infinity; /* the minimum item to be returned */
int i, j, MinTree; /* MinTree is the index of the tree with the minimum item */
if ( IsEmpty( H ) ) { PrintErrorMessage(); return –Infinity; }
for ( i = 0; i < MaxTrees; i++) { /* Step 1: find the minimum item */
if( H->TheTrees[i] && H->TheTrees[i]->Element < MinItem ) {
MinItem = H->TheTrees[i]->Element; MinTree = i; } /* end if */
} /* end for-i-loop */
DeletedTree = H->TheTrees[ MinTree ];
H->TheTrees[ MinTree ] = NULL; /* Step 2: remove the MinTree from H => H’ */
OldRoot = DeletedTree; /* Step 3.1: remove the root */
DeletedTree = DeletedTree->LeftChild; free(OldRoot);
DeletedQueue = Initialize(); /* Step 3.2: create H” */
DeletedQueue->CurrentSize = ( 1<<MinTree ) – 1; /* 2MinTree – 1 */
for ( j = MinTree – 1; j >= 0; j – – ) {
DeletedQueue->TheTrees[j] = DeletedTree;
DeletedTree = DeletedTree->NextSibling;
DeletedQueue->TheTrees[j]->NextSibling = NULL;
} /* end for-j-loop */
H->CurrentSize – = DeletedQueue->CurrentSize + 1;
H = Merge( H, DeletedQueue ); /* Step 4: merge H’ and H” */
return MinItem;
}
